
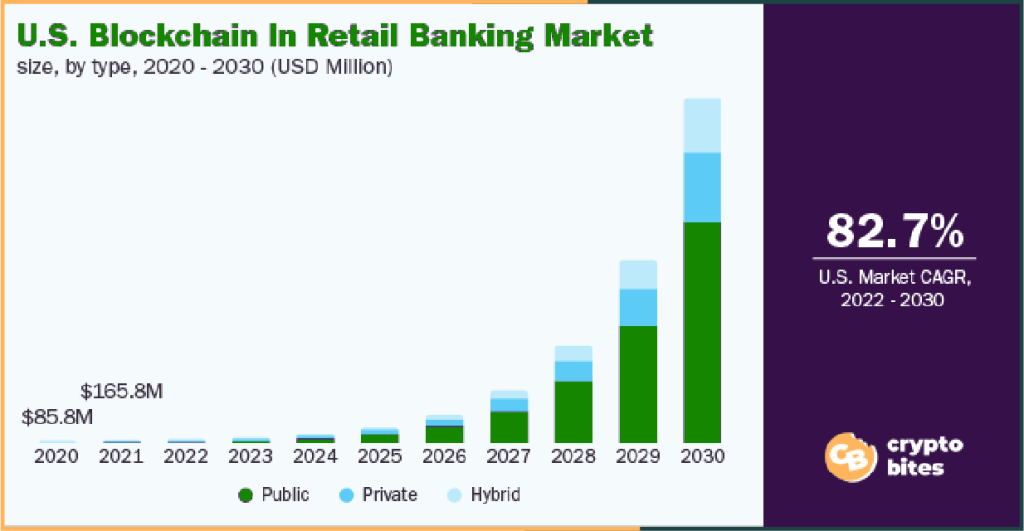
Hybrid Blockchain – Benefits of a Combined System
Blockchain is gaining traction across enterprises, governments, and various organizations as a way to manage data more efficiently. However, when it comes implementation, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
You’ve probably heard of two main types: public and private blockchains. Public ones are open for all to see, while private ones keep things more restricted.
But there’s another option: hybrid blockchains. They blend elements from both public and private blockchains to create something unique. While they might not be as common, hybrid blockchains offer a middle ground for those seeking a balance between transparency and control.
Now, I’ll be exploring hybrid blockchain and its benefits. I’ll take a close look at what exactly a hybrid blockchain is and why it’s worth your attention!
Key Takeaways
- Hybrid blockchain blends public and private features for balanced security and transparency.
- Customizable architecture enables controlled access, fostering collaboration.
- Applications span finance, supply chain, government, and energy sectors.
- Benefits include closed ecosystem operation, flexibility, defense against attacks, and low costs.
- Drawbacks: centralization risks, security concerns, adoption challenges, scalability issues.
What is Hybrid Blockchain?
A hybrid blockchain blends features from both private and public blockchains, creating a unique composite. In this setup, transaction data is initially verified through a public blockchain’s consensus process, making it accessible to all. However, the information is then stored on a private blockchain, accessible only to authorized users.
This combination offers a balance between security, privacy, and transparency, making it suitable for applications in supply chain management, finance, and governance.
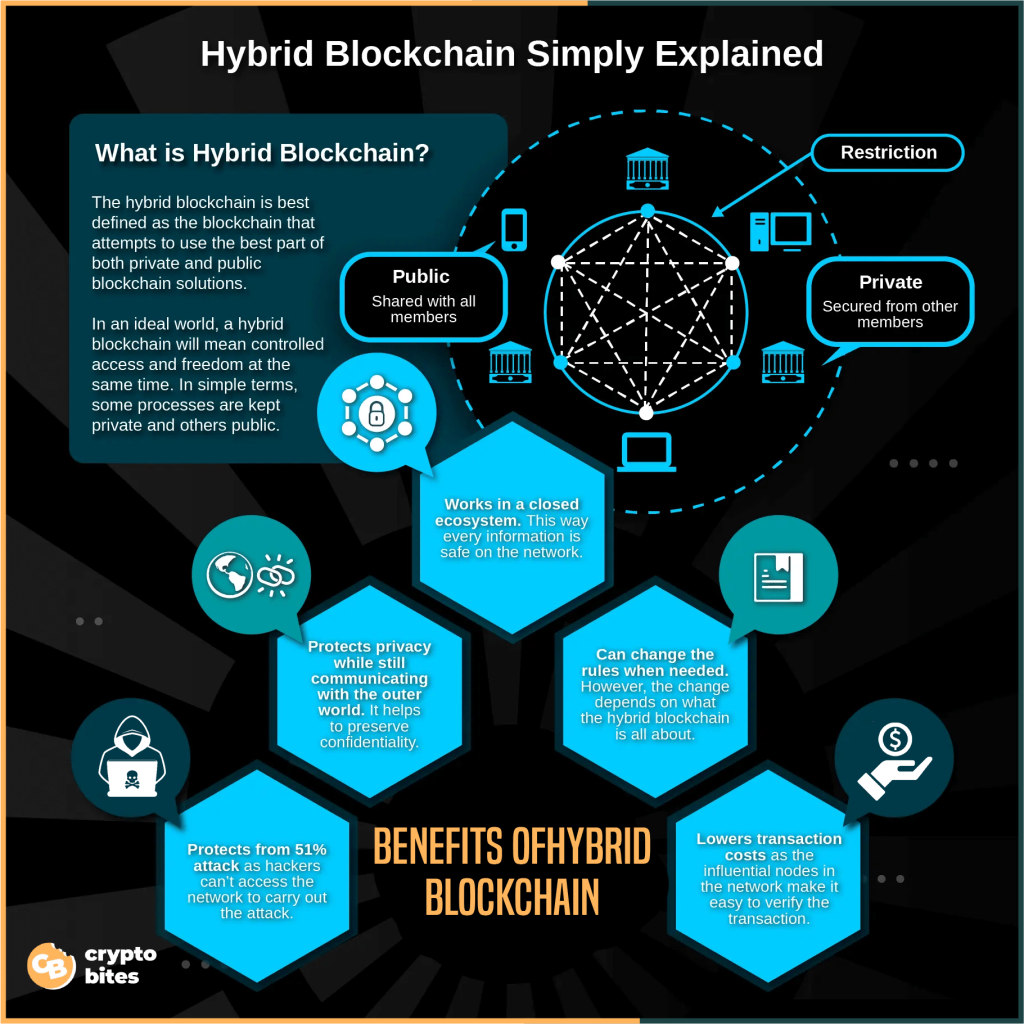
The architecture of a hybrid blockchain is highly customizable, allowing members to control access and visibility of transactions. This flexibility enables businesses to collaborate effectively with stakeholders, taking the advantage of the strengths of both public and private blockchains.
To better understand hybrid blockchain, exploring various projects in this space is recommended. One notable example is XDC, developed and operated by Singapore-based company XinFin. XDC leverages blockchain technology across public and private levels, showcasing the potential of hybrid blockchain solutions.
Hybrid Blockchain Uses Cases
Let’s find out some real life applications hybrid blockchain in different industries:
1. IoT
IoT devices connected through OneDrive Cloud Computing are at risk of being hacked due to their wireless nature. Hybrid blockchains mitigate these risks by combining features from public and private blockchains, providing better security against data breaches and unauthorized access. Additionally, hybrid blockchains facilitate effortless collaboration among IoT devices through smart contract-based integration, ensuring all user data remains confidential and protected.
2. Banks
Hybrid blockchains offer a practical solution for banks, providing a middle ground to safeguard customer information while effectively managing internal operations. This adaptable approach makes them an appealing choice for financial institutions. Additionally, even specialized centralized cryptocurrencies like Ripple could potentially benefit from transitioning to a hybrid blockchain network.
3. Supply Chain
Given the intricate nature of supply networks, which demand both security and flexibility, neither purely public nor purely private blockchains will work out. As a result, many logistics firms within the supply chain industry have started integrating hybrid blockchain technology to optimize their operations.
4. Governments
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform government operations, and governments worldwide are taking notice. They’re beginning to integrate blockchain into various administrative functions, leveraging its capabilities in recording complex data, conducting elections, establishing public identity databases, automating acquisitions, providing social and humanitarian aid, and more.
To enable these applications effectively, the use of hybrid blockchains is essential. Hybrid blockchains strike a balance, giving governments the necessary control while also ensuring accessibility to the general population.
Fully private or public blockchains present limitations: they either restrict user access or expose excessive amounts of data. Hybrid blockchains offer the right level of control, allowing governments to maintain authority while utilizing the benefits of blockchain technology.
5. Business Corporations
Businesses can use hybrid blockchain technology to automate processes and enhance service dependability, trust, and transparency for staff members and end customers in sectors like supply chain and aviation, among others.
6. Energy
The application of hybrid blockchain technology can actually make the energy industry safer and more efficient. Energy transactions can be securely managed, and access to energy data can be restricted to authorized parties, enhancing confidentiality and security, thanks to the adaptable nature of the hybrid blockchain.
Simultaneously, the public blockchain can be used to establish an open ledger that tracks energy flow and ensures equitable distribution of energy resources. This transparent system promotes accountability and fairness, benefiting both consumers and energy providers.
Advantages of Hybrid Blockchain
I’ve already highlighted the various sectors where hybrid blockchain technology is being employed. There must be compelling reasons why it’s being adopted so widely. Well, here are a few perks that explain why it’s such a big deal:
1. Functions in a Closed Ecosystem
One of the key advantages of hybrid blockchain technology is its ability to operate within a closed ecosystem. This means that businesses or organizations can deploy blockchain technology without worrying about information leaks.
2. Flexibility in Rule Adjustment
The beauty of hybrid blockchain lies in its flexibility to adjust rules as needed. The specific modifications required depend on the objectives of the hybrid blockchain. For instance, in a hybrid system managing band registry or user identity verification, don’t expect frequent updates to data or transaction modifications.
3. Defense Against 51% Attacks
Hybrid blockchain provides strong protection against 51% attacks because hackers are unable to access the network to execute such an assault. This inherent security feature makes hybrid blockchain impervious to this type of attack.
4. Maintaining Outside World Relevance While Preserving Privacy
While private blockchain technology effectively addresses privacy concerns, its capability to communicate with the outside world is limited. Many businesses prioritize privacy but also need their blockchain to interact with all stakeholders, including the general public.
5. Comparatively Lower Transaction Costs
Another advantage of adopting hybrid blockchain is its low transaction costs. Transactions remain inexpensive because minimal nodes are required for verification. The strongest nodes in the network simplify the verification process, even for transactions on the public blockchain that may involve thousands of nodes. This efficiency can result in significant savings, with transaction fees as low as 0.01 dollars.
Limitations of Hybrid Blockchain Technology
Despite its numerous benefits, hybrid blockchain technology also comes with some drawbacks compared to conventional public and private blockchains. Let’s explore a few of these drawbacks:
1. Centralization
One significant drawback of hybrid blockchain technology is the need for a central authority to manage the private blockchain component. This centralized control can potentially compromise the security and openness of the system. Users may become wary of a centralized authority governing the private blockchain, leading to trust issues and concerns about the integrity of the system.
2. Scalability
Although hybrid blockchain technology offers greater scalability compared to traditional public blockchains, performance issues may arise as the network’s workload increases significantly. This could lead to reduced efficiency and slower transaction times, impacting the overall effectiveness of the technology.
3. Early Adoption Stage
The adoption of hybrid blockchain technology is still in its early stages. Organizations may encounter challenges in acquiring the necessary knowledge and resources to establish and operate a hybrid blockchain network due to the lack of standards and widespread adoption.
Final Thoughts
While blockchain technology offers tremendous potential, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. For businesses and organizations seeking to capitalize on the benefits of blockchain without compromising their confidentiality, hybrid blockchain would be an appropriate solution .
Combining the strengths of public and private blockchains, hybrid blockchain offers a balanced approach, providing security, privacy, and transparency, all at the same time.
As industries grapple with data management and security challenges, hybrid blockchain appears to be a promising avenue forward, offering a flexible and pragmatic solution in the evolving landscape of blockchain technology.




