Hybrid Blockchain vs Consortium Blockchain – 4 Key Differences
As the popularity of Bitcoin and other cryptos continues to soar, companies are increasingly transitioning their blockchain initiatives from theoretical concepts to practical implementations. Deloitte’s 2021 Global Blockchain Survey, which gathered insights from 1,280 senior executives across 10 locations, revealed that nearly 80% of respondents view digital assets and their underlying blockchain technologies as pivotal to their industries in the near future.
However, navigating the blockchain landscape isn’t a one-size-fits-all work. With various blockchain types tailored for unique use cases, including public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains, companies must carefully weigh the advantages, disadvantages, and optimal applications of each system.
Right now, I will talk about hybrid and consortium blockchain and how they differentiate.
Let’s dive right in!
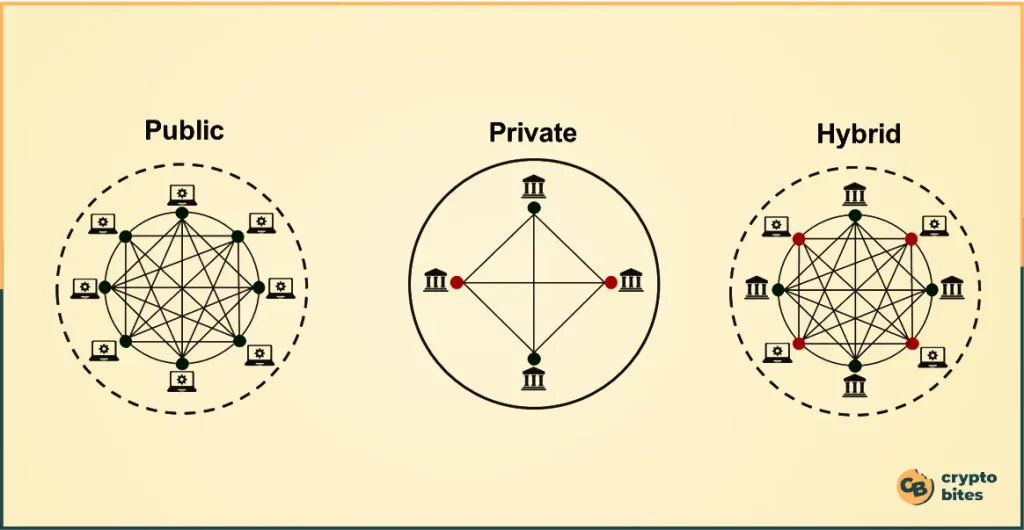
What is Hybrid Blockchain?
A hybrid blockchain is a unique blend of both public and private blockchains, designed to harness the strengths of each while mitigating their respective weaknesses.
In this setup, you’ll find a mix of public and private entries within the database. Public nodes operate much like those in traditional public blockchains, open for anyone to join and participate in the network. Meanwhile, private nodes are overseen by specific entities or individuals, responsible for verifying and scrutinizing transactions.
This dual nature allows a hybrid blockchain to offer a range of benefits. Private nodes make transactions execute faster, more securely, and with greater privacy.
Meanwhile, the inclusion of public nodes ensures decentralization and transparency, making it challenging for any single entity to maintain control over the network.
In a hybrid blockchain, network members have the authority to determine who can access the network and which transactions are visible to the public. This flexibility enables better governance and privacy controls, offering a versatile solution to meet various business needs.
Benefits of Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchain has a wide range of benefits, making them one of the most reliable blockchain technologies right now:
1. Hybrid Blockchain is a Closed Ecosystem
A hybrid blockchain offers a closed ecosystem where user anonymity is preserved within the network. This means that while the user’s identity is concealed from the public, it is known to authorized members of the network. This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations that require confidentiality but still want to maintain some level of transparency within a select group.
Example: in a healthcare hybrid blockchain, patient identities can be kept anonymous to the public while being accessible to verified medical professionals and institutions within the network.
2. Data Security
Hybrid blockchains provide stronger data security compared to public blockchains. The permissioned nature of these networks ensures that transactions are protected and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. This significantly reduces the risk of security breaches, including the notorious 51 percent attacks that can occur in less secure networks.
Example: A financial institution using a hybrid blockchain can ensure that sensitive transaction data is only accessible to verified parties, thereby preventing exposure to potential cyber-attacks and ensuring the integrity of financial records.
3. Increased Interoperability
Hybrid blockchains excel in providing seamless connectivity with other blockchain networks, which is a crucial feature for modern digital ecosystems. This interoperability allows for the efficient transfer of assets and data across various platforms, enabling different blockchain networks to communicate and collaborate without friction.
Hybrid blockchains, therefore, offer a flexible infrastructure that supports the diverse needs of businesses, allowing them to operate across multiple blockchain platforms without compromising on security, privacy, or efficiency.
Example: A business that operates on a hybrid blockchain can easily interact with both private and public blockchain networks. For instance, a company could use a private blockchain for internal record-keeping while also participating in a public blockchain for customer transactions. This interoperability ensures that the company can leverage the strengths of different blockchain technologies as needed.
4. Reduced Transaction Costs
Hybrid blockchains combine the advantages of public blockchains with greater control over data. This dual approach allows organizations to enjoy the decentralized features of public blockchains while also having the authority to govern their own data. As a result, the overall cost of deploying and maintaining a hybrid blockchain is often lower than that of a fully private blockchain. Transaction fees can potentially be as low as $0.01 per transaction, making it more cost-effective for businesses.
Example: A supply chain management company can utilize a hybrid blockchain to track shipments and transactions. The public aspect allows for transparency and traceability for end consumers, while the private aspect keeps sensitive business data secure. This balance can lead to significant cost savings compared to operating a completely private blockchain system.
5. Faster Operations and Ease of Management
Hybrid blockchains are like a fast train for transactions. They move quickly and smoothly, making sure businesses can keep up with lots of sales or deals without getting bogged down. Plus, they’re not too complicated to manage, which means less headache for the people running them.
Example: Imagine a big store during a holiday sale. It’s super busy, and they need to make sure every purchase is tracked fast. A hybrid blockchain would be like having a super-efficient cashier who never makes a mistake, keeps everything in order, and works at lightning speed. That way, the store can focus on selling and not worry about keeping track of everything
6. Privacy Protection
Hybrid blockchains strike a good balance between transparency and privacy. They offer better visibility into transactions than private blockchains, which tend to be more closed off. This means that while hybrid blockchains keep certain information protected, they also allow for a greater degree of openness about the activities taking place on the network.
Example: Think of a company that wants to share its supply chain data with its suppliers to ensure better coordination but doesn’t want its competitors to see this information. A hybrid blockchain can provide this level of selective transparency, which is not typically possible with a private blockchain that restricts all access to insiders.
What is Consortium Blockchain?
The consortium blockchain emerges as a groundbreaking solution, seamlessly blending the openness of public blockchains with the confidentiality of private ones.
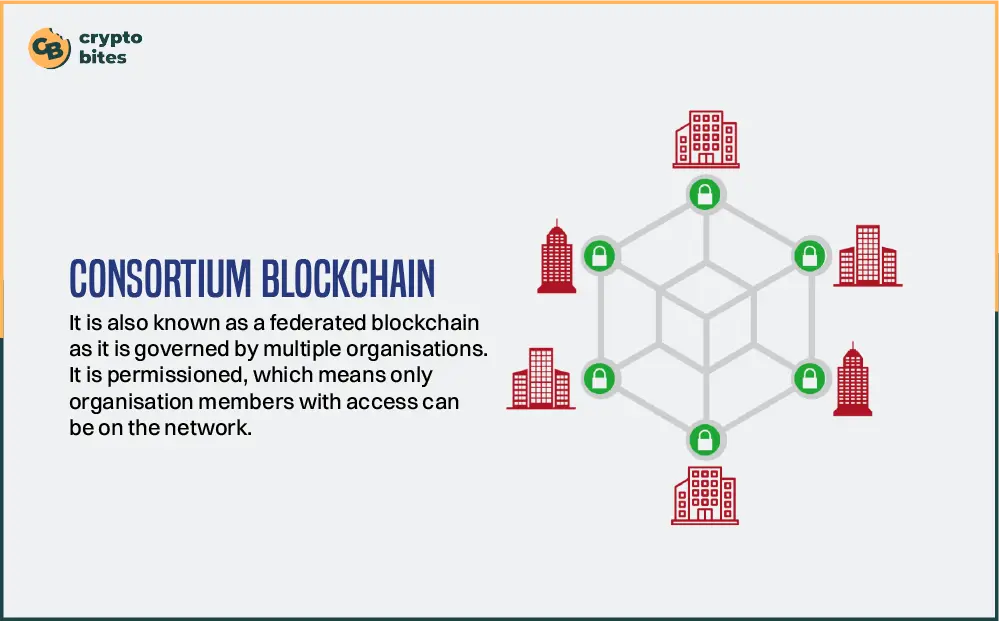
Consortium blockchain serves as a collaborative platform where multiple companies can come together, maintaining control over the network while ensuring heightened privacy and efficiency—a game-changer for businesses seeking secure interactions without compromising autonomy.
- Hybrid Model: In a consortium blockchain, elements of both private and public blockchains coalesce into a hybrid model.
- Shared Governance: This setup facilitates shared governance and restricted access among a select group of organizations, ensuring that no single entity holds unilateral authority.
- Selective Membership: Consortium blockchains limit network participation to a small, trusted cohort of entities.
- Enhanced Security: Unlike public blockchains, which are open to all, the deliberate selection process of consortium blockchains enhances security and operational efficiency, making it an ideal fit for corporate applications where stringent control is paramount.
- Controlled Decentralization: Despite their decentralized architecture, consortium blockchains offer a level of control akin to private blockchains. This unique combination streamlines decision-making processes while nurturing trust among participants, paving the way for smoother collaboration and innovation within the network.
Benefits of Consortium Blockchain
Similar to hybrid blockchain, consortium blockchain also possess tonnes of benefits. Here are some benefits that make it unique:
1. Cooperation
Consortium blockchains enable collaboration among groups with shared objectives on a common platform. This leads to improved cooperation and more effective resolutions, as stakeholders work together towards common goals.
2. Lower Expenses
By leveraging a shared platform, businesses within a consortium can reduce the costs associated with building and maintaining independent systems. This collaborative approach helps in optimizing resources and streamlining operations, resulting in cost savings for all participants.
3. Increased Scalability
Unlike individual organization’s blockchain networks, consortium blockchains offer greater scalability. With multiple entities contributing to the network, it can handle a higher volume of transactions efficiently, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
4. Stronger Security
Consortium blockchains are permissioned networks, meaning only approved users have access. This inherent permissioning strengthens security by restricting unauthorized access and ensuring that sensitive data remains protected within the network.
5. Better Governance
Blockchain consortiums enable groups of organizations to establish governance structures, allowing them to make collective decisions and set rules for the network. This democratic governance model ensures transparency, fairness, and alignment of interests among consortium members.
Hybrid Blockchain vs Consortium Blockchain – Comparison Table
The table below shows the unique natuer of each blockchain and the differences between the two:
| Feature | Hybrid Blockchain | Consortium Blockchain |
| 1. Decision-making Process | Incorporates characteristics of both public and private blockchains. Some decisions can be centralized, while others decentralized. | Decision-making authority lies with a predetermined consortium. Collectively sets rules and validates transactions. |
| 2. Accessibility Across Blockchain Types | Offers flexible accessibility, balancing public and private blockchain attributes based on data or transaction nature. | Controlled accessibility limited to consortium members, ensuring a closed and secure environment. |
| 3. Scalability | Extensive scalability due to the blend of public and private elements, equipped to handle larger volumes of participants and transactions. | While potentially limited in participants, it offers swift transaction processing times within its network. |
| 4. Control Dynamics in Blockchain | Predominantly controlled by a singular organization, yet retains elements of decentralization for nuanced control dynamics. | Control is evenly distributed among consortium members, promoting collaborative control mechanisms. |
These differences highlight the unique features and functionalities of each blockchain model, catering to diverse needs and preferences within different industries and use cases.
Similarities Between Hybrid Blockchain and Consortium Blockchain
Despite the minor differences, there are more similarities between hybrid and consortium blockchains than differences. Here are some of the ways they’re similar:
1. Flexibility in Transparency
Both hybrid and consortium blockchains offer a degree of flexibility in transparency. Participants have the ability to select which transactions or data they want to make public and which they want to keep private. This adaptability allows for tailored transparency, catering to the specific needs and preferences of the involved parties.
2. Security Features
In comparison to fully public blockchains, both hybrid and consortium blockchains boast improved security features. Their semi-private nature offers heightened security and reduces the risk of malicious activity and unauthorized access. By restricting access to a defined group of participants, these blockchains mitigate the potential for external threats, ensuring a more secure environment for transactions and data management.
3. Adherence to Regulations
The semi-private architecture of both hybrid and consortium blockchains lends itself to better compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. This flexibility ensures that users can comply with relevant laws without compromising the integrity of the blockchain network. By allowing for controlled access and customizable transparency, these blockchains enable organizations to navigate regulatory requirements while maintaining the security and reliability of their transactions and data.
4. Effectiveness
Both consortium and hybrid blockchains are designed to facilitate faster transaction processing compared to fully public blockchains. By incorporating elements of both public and private networks, or by restricting access to a defined group of users, these blockchain architectures optimize transaction throughput and minimize latency. This emphasis on efficiency enhances overall operational effectiveness, making consortium and hybrid blockchains well-suited for use cases where speed and reliability are paramount.
Hybrid vs Consortium – Which One Should You Go For?
Before deciding between hybrid and consortium blockchains, it’s crucial to understand the unique features and considerations of each. Here’s a breakdown of key factors to consider when choosing the right blockchain model for your project:
1. Use Case
Determine the purpose of the blockchain and the requirements it needs to fulfill. Hybrid blockchains may be more suitable for applications that require a balance between privacy, security, and scalability, while consortium blockchains may be preferred for collaborative projects involving multiple trusted parties.
2. Privacy Requirements
Evaluate the level of privacy needed for your transactions and data. If you require a higher level of privacy while still maintaining connectivity with external parties, a hybrid blockchain might be more appropriate. However, if you need to collaborate with a select group of trusted participants while maintaining confidentiality, a consortium blockchain could be the better choice.
3. Scalability
Consider the potential growth of your network and the scalability requirements. Hybrid blockchains may offer greater scalability due to their combination of public and private elements, while consortium blockchains may have limitations based on the number of participants allowed in the network.
4. Security
Assess the security needs of your project and the importance of control over the network. Both hybrid and consortium blockchains provide enhanced security compared to fully public blockchains, but the level of control and decentralization may vary between the two options.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Determine whether your project needs to comply with specific regulations or industry standards. The adaptable nature of consortium blockchains may make them more suitable for industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
To Sum Up
Carefully evaluating your project’s requirements and considering factors such as use case, privacy, scalability, security, and regulatory compliance is essential when choosing between hybrid and consortium blockchains. I’d suggest you to have an in-depth understanding of the unique features of each blockchain model, to make an informed decision that aligns with your project’s goals and objectives.




