
What is a DAO? Secret Technology That’s Shaping the Future Economy
Picture a world where companies are run by a community of people, all collaborating and making decisions together, without any centralized authority like a CEO or a board of directors calling the shots.
Well, that’s what DAO is all about. It’s the hot new thing in the blockchain space that is shaking up the traditional corporate governance and digital economy model.
If you’re curious about DAOs and want to learn more about how they’re changing the game in the world of corporate governance, you’re at the right place.
Because today, we’ll dive into the world of DAOs, exploring how they work and their potential impact on the future of business.
What Exactly is a DAO?
In simple terms, a DAO or Decentralized Autonomous Organization is a collectively owned organization run by its members using blockchain technology. It’s like a digital company that exists on the internet and allows its members to propose, vote on, and fund projects systematically.
Much like crowdfunding, DAOs can be used to collect investments for any potential business venture. However, unlike crowdfunding projects, all the investors in a DAO have equal authority to make business decisions. This completely wipes out any possibilities of scams, something that happens a lot with crowdfunding.
So, in DAOs, you’re more likely to have serious, business-minded individuals collaborating on a project, pooling their investments, and using those funds to achieve something profitable in a completely secure and transparent manner.
Think of it as a community garden where you and other members come together to plant, tend, and harvest crops. Each member has a say in what gets planted, how resources are allocated, and how the garden is managed. In other words, there is no one person in charge; instead, decisions are made through discussion and consensus.
How to Turn Profitable Business Ideas Into Reality with DAO
Here is a little example of how you can use DAO in real-life settings:
Imagine you came across a successful website blog that is up for sale at a great price. You believe that with some investment and effort, you can improve its content and implement effective SEO strategies to increase its value. You estimate that you can sell it for a huge profit, around $30,000 to $40,000, which would be three to four times your initial investment of $10,000.
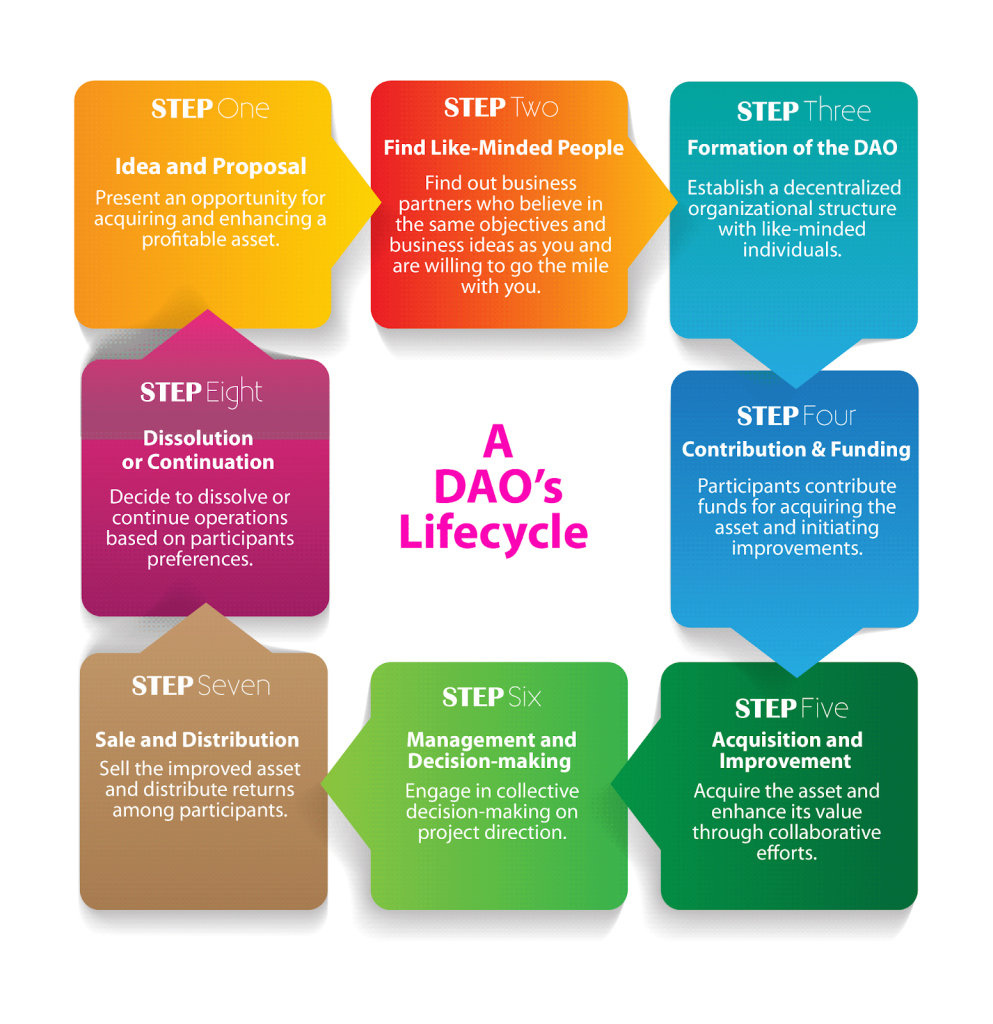
However, if you don’t have enough funds or prefer to share the risk with others, you can pitch this opportunity to your network on Facebook or LinkedIn and establish a DAO together.
If you can find only 10 like-minded people, each contributing $1,000, you can start your project right away. When the blog eventually sells for the projected $40,000 after further improvements, and increased traffic, each participant will receive a substantial return of $4,000.
This is how you can turn your profitable business ideas into reality simply by using DAO.
How is It Any Different From Typical Companies?
To get why DAOs are such a big deal, you’d have to truly understand how traditional companies work.
In a typical corporate structure, you have the top authorities, such as the CEO or the board of directors as decision-makers. These decisions are then passed down to managers and employees who carry out the work required to achieve the predetermined objectives.
However, innovation, creativity, and new ideas from lower-level employees are dismissed as it’s a hierarchical system that only values decisions made at the top of the chain.
The potential for corruption at the highest levels of management is one of the biggest challenges for corporate entities. Take, for instance, the FTX scam. Sam Bankman Fried, FTX CEO, is a prime example, who misused his power to steal around a staggering $8 Billions in customer funds.
Fraud, embezzlement, and insider trading are all on the table with a corrupt executive. Why so? Because as you’ve read earlier, most of the CEOs and other top executives have unchecked power and control over the company. And they’re equipped with the authority to do almost everything they want with very less resistance or accountability.
Whereas someone at the bottom end of the corporate ladder, your opinions will be of zero value. This has devastating consequences for shareholders, employees, and the broader economy.
This is where DAOs come in – they offer a new way of organizing and operating that is decentralized and collaborative. In a DAO, decision-making is distributed across all organization members rather than being concentrated in the hands of a single leader. All members of a DAO have an equal say in decision-making, and proposals can be submitted and voted on by anyone in the organization.
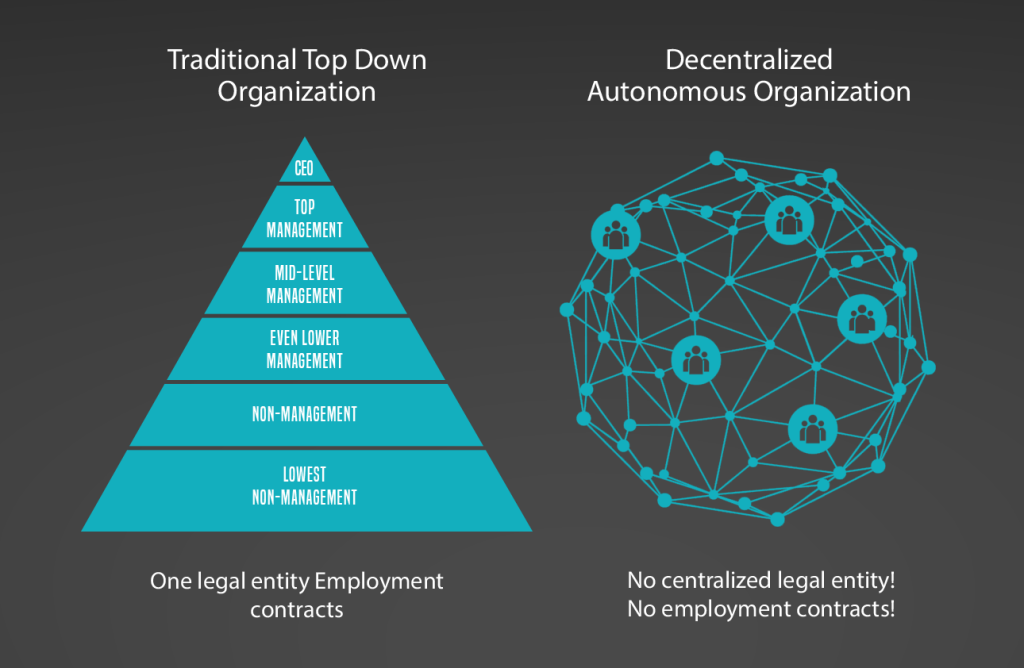
Let’s turn to an analogy to simplify this comparison.
A Typical corporate structure or a company is like an orchestra where the conductor is the CEO. The conductor decides how the music will be played and dictates the parts to each musician. The musicians (employees) then play their assigned parts as directed by the conductor. The problem is that the musicians have little to say in how the music is composed or played. Even if a musician has a brilliant idea, it’s unlikely to be implemented unless the conductor agrees.
A DAO, on the other hand, is like a jazz band. There is no single leader; every member has an equal say in what songs to play and how to play them. Any member can suggest a new tune or improvise on the melody. Decisions are made collectively through discussion and consensus. When a new idea emerges, the whole band incorporates it seamlessly into the performance. There is more flexibility, creativity, and improvisation because everyone has a voice and contributes their ideas.
How Do DAOs Work?
DAOs operate on a blockchain network and are governed by smart contracts. They leverage blockchain technology and smart contracts to create decentralized and transparent decision-making and resource management systems.
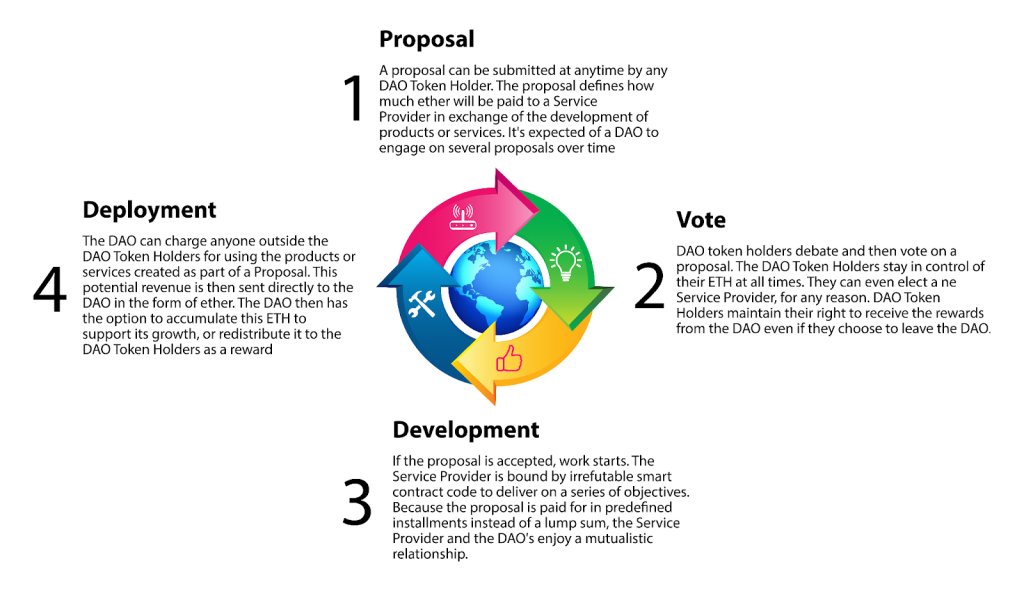
Here’s a detailed breakdown of their operation:
Decentralized Governance Structure
DAOs have a decentralized governance structure, where decision-making authority is distributed among the participants. The governance model can vary but typically involves token holders with voting rights. Each token represents a share of ownership and voting power within the organization. Token holders can propose and vote on decisions, such as changes to the DAO’s rules, allocation of resources, or project funding.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are like self-executing digital agreements that automatically enforce and execute predefined terms and conditions. Picture a vending machine that gives you a snack when you insert the correct amount of money. The machine is programmed like this: if you provide the exact amount of money, it releases the snack.
Similarly, smart contracts within a DAO carry out actions, such as transferring funds or assets, when specific conditions are met. For example, a smart contract might dictate that funds can only be transferred if most token holders approve the transaction.
Transparency and Trust
One of the key benefits of DAOs is transparency. Since all transactions and changes are recorded on the blockchain, they are visible to all participants. Just like collaborating on a Google Doc with a team, each change made to the document is recorded and visible to everyone involved.
In a blockchain, transactions are similarly recorded and visible to all parties, ensuring transparency. What sets it apart is that changes can only take effect if a majority of users approve them, making the blockchain secure and transparent and reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Consensus Mechanisms
DAOs rely on consensus mechanisms to reach agreements and make decisions. Depending on the DAO’s design, this could involve various methods, such as simple majority voting, quadratic voting, or other governance mechanisms. The consensus mechanisms aim to ensure that decisions reflect the collective will of the participants and prevent the concentration of power in a few individuals’ hands.
Resource Allocation
DAOs can manage and allocate resources, such as funds or assets, based on the consensus of the participants. For example, a DAO focused on funding open-source projects may allow token holders to propose project ideas and vote on which projects receive funding. Smart contracts can automatically distribute funds to approved projects based on the voting outcomes.
Evolution and Upgrades
DAOs can evolve and upgrade over time through community-driven decision-making. The token holders can propose, discuss, and vote upon changes to the DAO’s rules or smart contracts. This flexibility allows the organization to adapt to changing circumstances and improve its functionality as needed.
For instance, imagine a DAO running a decentralized crowdfunding platform. As the platform grows, token holders may propose improvements like enhancing the user interface or implementing additional security measures.
Through community discussions and voting, the proposed upgrades that receive majority support are implemented by modifying the DAO’s rules or smart contracts. This allows the organization to adapt and provide a better user experience as it evolves over time.
How to Create Your Own DAO?
Do you have an idea that can have a positive impact on the world? If so, DAOs can help bring your ideas to life. Big ideas rarely come to fruition with just one person; you need a team and funding. So, how can you use DAOs for all of that? Here’s a brief step-by-step process.
First, you need to develop your own idea that would attract people. While it helps if it’s something that nobody has ever tried before, it doesn’t always have to be too unique or fancy.
Here is someone who wants to start a simple DAO for renewable energy projects:
Once you have a working concept and a value proposition, you can pitch your idea to people. You can do this on social networking platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, or forums such as Reddit.
Once you have a community that shares the same goals as you, you’re halfway there. And guess what? You don’t even need a thousand people to start a DAO. You can start small, even with 5-10 people or fewer. All you need to do is specify the type of DAO, set the rules and deploy.
You can opt for an investment DAO, which raises capital for DeFi projects and startups. Alternatively, you can go for a Social DAO that fosters social networking in the crypto community, offering a platform for communication, idea sharing, and fundraising.
In the next stage, you’d have to set the rules for the DAO as to how it will function much similar to a constitution of a country that governs its fundamental regulations.
Once you’re done with all that, you can build and deploy the DAO, collect investments, and start working on your predefined projects. In the case of the energy project I just mentioned, the DAO’s founder and group members may assess and acquire potential sites, use the treasury funds to purchase solar panels and hire experts to set up the solar systems.
If the solar systems are set up correctly, they should generate a substantial energy and sell it to the grid and retain profits. The profits will then be divided equally among the shareholders and securely and transparently sent back to their respective wallets using the DAO.
This is how you can easily conceptualize and implement your strategies to give shape to your dreams using DAO.
Real-World Examples of DAOs
To provide a better understanding, let’s explore some real-world examples of DAOs:
CityDAO
CityDAO is a DAO created to collectively own and manage land. It raised over six million dollars from 5,000 people through its governance token called “Citizenship” and managed to buy 40 acres of land near Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming.
The DAO members, or the “citizens” as they call it, have the power to vote on various decisions, such as the location of the next piece of land to acquire and what gets built on the land.
But CityDAO isn’t just about buying land. The main goal is to make a decentralized city where decisions are made together, and more people can benefit. CityDAO is a real-life example of a DAO that wants to change how cities are governed and owned.
The DAO
The DAO’s story stands out as one of the most captivating and noteworthy stories within the cryptocurrency community.
The DAO was a groundbreaking project built on the Ethereum blockchain. A staggering $150 million of Ether was raised, the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, from more than 11,000 individual investors. This made it one of the largest crowdfunding campaigns in the history of all time.
The concept of The DAO was exciting for many because it promised to revolutionize traditional investment models by eliminating the need for intermediaries and allowing direct participation and control by token holders.
However, shortly after The DAO’s launch, a critical vulnerability in its code was discovered. This vulnerability allowed an attacker to exploit a loophole and siphon off approximately $50 million worth of Ether, which led to panic and confusion within the cryptocurrency community.
Ultimately, the Ethereum community agreed to perform a “hard fork” to rectify the situation. A hard fork involves creating a new version of the blockchain with updated rules to reverse the theft and restore the stolen funds to their rightful owners.
This decision was controversial and resulted in a split within the Ethereum community, leading to the creation of Ethereum Classic, a separate blockchain that continued to recognize the pre-fork Ethereum as the legitimate chain.
ConstitutionDAO
ConstitutionDAO aimed to buy an original copy of the US Constitution. It raised over 47 million dollars in seven days to participate in an auction at Sotheby’s auction house. Although ConstitutionDAO was outbid and did not win the auction, it illustrates the potential of DAOs to pool resources for collective endeavors.
Benefits of DAOs
DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations) offer several benefits over traditional organizations, including:
Collective Ownership and Incentives
DAOs often issue governance tokens that give holders voting rights and the opportunity to influence the organization’s activities. This ownership structure allows participants to align their interests and actively contribute to the DAO’s growth. For instance, PleasrDAO gives its members exclusive rights to an unreleased Wu-Tang Clan album, providing unique ownership and incentives within the community.
Increased Transparency and Accountability
DAOs use blockchain technology, which offers a transparent and auditable ledger of all transactions and decisions. This transparency helps build trust among members and external observers. Anyone can verify the organization’s financials and activities. CityDAO, for example, keeps its funds in a public blockchain treasury accessible to all, ensuring transparency in income and spending.
Access to Capital and Investment Opportunities
DAOs provide a mechanism for pooling resources and accessing capital from various individuals. This democratizes investment opportunities and allows smaller investors to participate in projects previously restricted to high-net-worth individuals. ConstitutionDAO, for example, raised millions of dollars in a short time frame to bid on an original US Constitution copy.
Flexibility and Adaptability
DAOs are highly adaptable and can evolve with changing circumstances. They can easily incorporate new members, adjust their governance structures, and pivot their activities based on the consensus of the community. This flexibility allows DAOs to respond to emerging opportunities and challenges. UkraineDAO, for instance, raised significant funds to donate towards the Ukrainian defense effort, showcasing the ability of DAOs to mobilize resources for important causes.
These benefits highlight the transformative potential of DAOs. They enable more inclusive decision-making, foster collaboration and innovation, provide ownership opportunities to a wider range of participants, and leverage blockchain technology to ensure transparency and accountability. DAOs are revolutionizing traditional organizational structures, opening up new possibilities for collective action and shared
Challenges of DAOs
While DAOs offer numerous benefits, they also face certain challenges that must be considered. Here are some key challenges associated with DAOs:
Lack of Legal and Regulatory Framework
The legal and regulatory framework for DAOs is still evolving, and it has a significant level of uncertainty and risk. This is mainly because DAOs are a relatively new concept, and many legal and regulatory questions remain unanswered. On the other hand, traditional corporations operate within an established legal and regulatory framework that has been in place for many years.
Requires Immense Technical Understanding
DAOs are entirely internet-dependent, requiring a certain level of technical understanding to operate effectively. This is because DAOs are built on blockchain technology, which is a complex and rapidly evolving field. In contrast, traditional corporations are not internet-dependent and require less technical understanding to operate. While many modern businesses rely on the internet to some extent, they can still function without it, unlike DAOs.
Tremendously Time-Consuming Decision Making
DAOs rely on collective decision-making, which can be complex and time-consuming. Reaching consensus among a large number of participants with varying opinions and interests can be challenging. Making decisions may require extensive discussions and voting processes, potentially resulting in slower response times than traditional hierarchical structures.
Coordination and Execution Barriers
Coordinating activities within a DAO can be challenging, especially when participants are geographically dispersed and have different levels of commitment. Ensuring effective collaboration, clear communication, and timely execution of projects may require additional efforts.
Security and Technical Risks
DAOs rely on blockchain technology, which introduces its own set of security risks. Smart contracts, which automate the execution of DAO operations, may be vulnerable to coding errors or exploitation by malicious actors. Hacks or vulnerabilities in the underlying blockchain infrastructure can also pose risks to the assets and operations of DAOs.
Lack of Reputation and Trust
The reputation and trust of a DAO can impact its ability to attract members, partnerships, and investment. Negative incidents, such as fraud, mismanagement, or controversies, can erode trust and undermine the DAO’s credibility.
Future of DAOs
The future of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) looks promising as they continue to gain traction and evolve in various ways. Below are two images, one from 2022 and one from 2023.
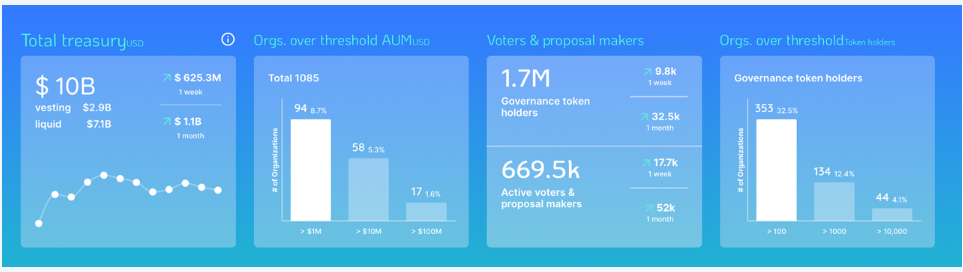
June 2022. Source: Deepdao.io
According to the data from June 2022, the total investment in DAOs was recorded at $10 billion. This already showcased substantial interest and investment in these decentralized organizations.
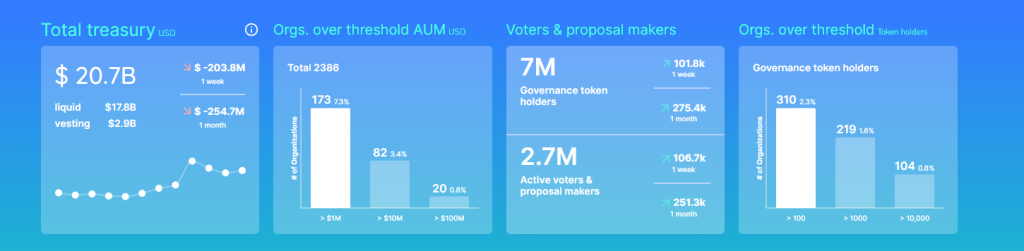
July 2023. Source Deepdao.io
Fast-forward to July 2023, and within just a year, the total investment in DAOs doubled to a whopping $20 billion. The doubling of investment in such a short period highlights the appeal of DAOs in providing more inclusive and transparent decision-making processes.
With this exponential growth in investment, it is clear that DAOs are gaining momentum and attracting attention from both individuals and institutions. The future of DAOs appears to be filled with opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and decentralized governance, as they continue to reshape traditional organizational structures and pave the way for a more democratic and participatory approach to decision-making.




