
Consortium Blockchain- Everything You Should Know
Around 3.9% of the global population is currently using blockchain technology, and therefore, it’s no longer just a buzzword.
But do all blockchain networks follow the same mechanism?
Not really. To bridge the gap between a public and a private blockchain, there’s consortium blockchain.
It is a kind of intermediary link between a private and a public blockchain network, allowing a preselected group of organizations to manage data more securely.
However, to find out more about its key features, use cases, benefits, and challenges, let’s dig deeper into consortium blockchain below.
Key Takeaways
- Consortium blockchain blends the best features of private and public blockchains to create a shared yet secured digital platform.
- Being partially decentralized, it strikes a balance between decentralization and controlled access.
- The network is distributed among a few preselected members from different organizations and all of them have an equal say in its governance.
- Fewer participants in a consortium can reach a consensus quicker, keeping the transaction speed higher and transaction cost lower.
What Is a Consortium Blockchain? How Does It Work?
A consortium blockchain, as opposed to a public blockchain, is a permissioned network. So, it’s more like a private blockchain.
But the key difference between consortium vs private blockchain is that consortium blockchain is not controlled by a single authority.
Rather, it’s constructed with a few preselected organizations, each with a private blockchain, having shared access over the entire network to control the consensus process.
Thus, it enhances trust and transparency among the participants while maintaining decentralization, the core concept of blockchain technology.
Being also known as the federated blockchain, it can multiply mutual trust and workflow among enterprises.
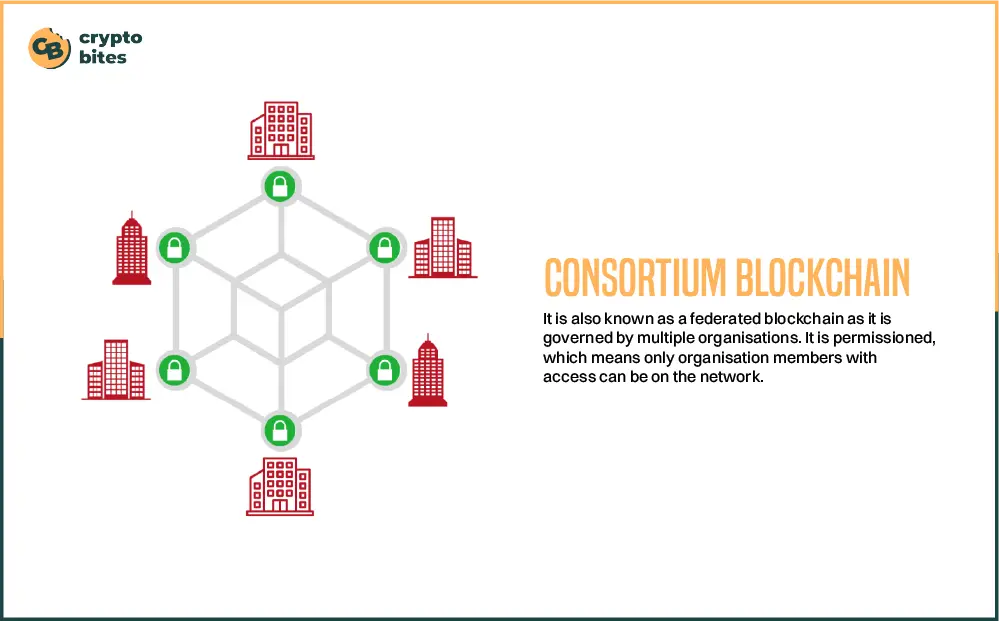
Suppose, 10 different financial institutions form a consortium blockchain for cross-functional collaboration. Each of the entities, known as a node, can equally contribute to the data management within the network, whether it’s about exchanging resources or validating transactions.
However, the number of nodes could be increased with the approval of the existing community. And for a new block within the network to be added, 8 of the 10 nodes must sign the block. Maintaining a democratic approach is how a blockchain consortium protects privacy while preserving decentralization.
Thanks to that, a consortium blockchain could be the best bet for corporations that must collaborate on a common platform without sacrificing data security to external parties.
Probably, that’s why, nearly 74% of organizations are choosing blockchain consortiums for their businesses, as Deloitte research shows.
Key Characteristics of Consortium Blockchain
As we delve more into this topic, let’s discuss the key characteristics of consortium blockchain in detail below.
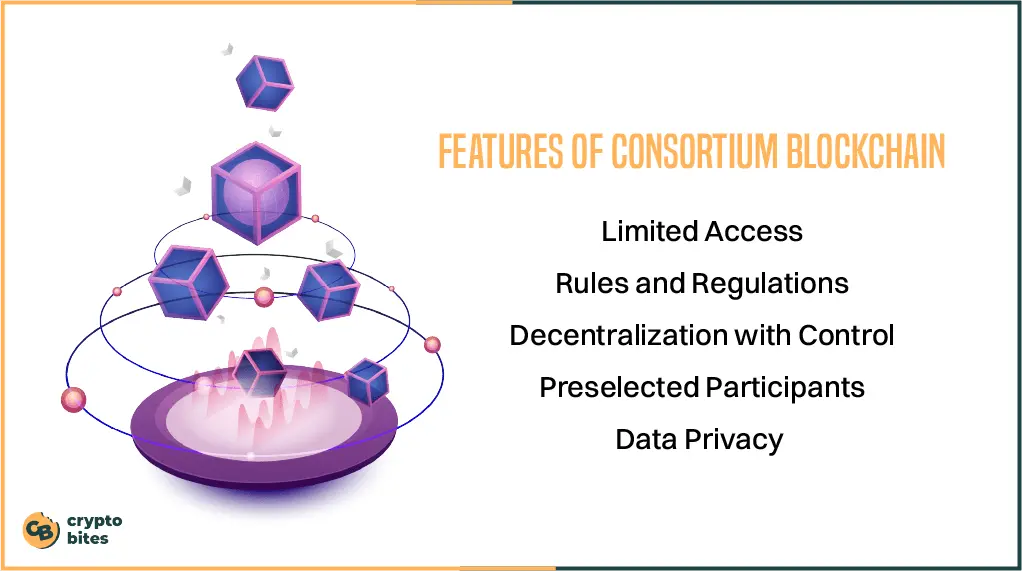
1. Limited Access
One of the standout features of this shared yet secured network is its restricted access. Only a predefined group of trusted members is allowed here, ensuring the privacy and security of the platform.
2. Rules and Regulations
Consortium blockchains aim to serve multiple businesses and organizations at a time. Therefore, all nodes must comply with the predefined set of rules and regulations to keep the framework’s creative juices flowing.
3. Decentralization with Control
The ecosystem of a consortium blockchain is decentralized by nature. All nodes across the network have an equal say in its governance, unlike the centralized authority of a private blockchain.
In addition, consortium blockchain consensus is crucial for a transaction to pass, and thus, it provides more control to the users compared to a public blockchain network.
4. Preselected Participants
As the network is accessible by only a few selected members, there are fewer risks of illegal or criminal activities. A small group of known participants, instead of a large number of anonymous nodes, makes this platform a secure choice for businesses and enterprises.
5. Data Privacy
A consortium blockchain is exposed to some limited individuals, and consequently, it upholds data privacy at its best. Each transaction is shared with authorized members only, eliminating any chances of compromise within the network. Also, the majority of the nodes must agree to change data or resources within the network.
Advantages of Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains, right now, are redefining the collaborative business approach by offering tons of benefits. Some of its major conveniences are as follows-
1. Faster Transaction Speed
The limited number of members on consortium blockchains ensures rapid-fire transactions due to fewer competing participants to verify transactions’ validity.
Moreover, the controlled user groups help reach a consensus in the consortium way faster than a public blockchain, keeping the transactional speed notably higher.
2. Cost-Effective Approach
Unlike a private blockchain, where a single authority maintains the entire network, a blockchain consortium relies on a cost-effective mechanism. Here, all the nodes equally share the maintenance cost of the platform.
3. No Chance of 51% Attack
All transactions within a blockchain consortium are safe from 51% attack as each of them is verified by specific members from multiple organizations.
Consequently, there is no way a single enterprise will gain 51% control over the network through collaboration with several others. Thus it seems nearly impossible to override or reverse any transaction for a particular entity.
4. Streamlined Collaboration
With a secured digital platform for multiple stakeholders, this innovative framework can streamline business collaboration by facilitating a cohesive ecosystem in the consortium.
As a result, member organizations within the network can collectively leverage its innovative applications for multifaceted business needs including cost reduction, decision-making, etc.
5. Scalability
As I already discussed, this is kind of a private database but is restricted to limited participants. That’s why the transactional speed is higher than a public blockchain network ensuring more scalability.
Because the preselected nodes have restricted access and can process transactions quickly, they can handle larger volumes of data more efficiently.
Disadvantages of Consortium Blockchain
Similar to any blockchain network, consortium blockchain also comes with some limitations. These are the challenges you can face while adopting consortium blockchain for your business-
1. Complex Infrastructure
A consortium blockchain’s central infrastructure is a bit complex to integrate with the existing ecosystems of multiple companies. It needs time and effort to create a standard network for several enterprises with the same protocols.
2. Conflict of Interests
As you already know, the authority of a consortium blockchain is distributed among a group of people from different organizations, and there are high chances of disputes over the governance of the network. Members of the network may have a conflict of interest when they value their own interests over the development of the chain as a whole.
3. Less Transparency
Only a few authorized members can check the validity of a transaction within a consortium. Thus it’s difficult for general people to verify the data/resources of the network.
That’s how consortium blockchains offer limited transparency compared to a public blockchain network.
4. Upgradation Challenges
With time, the number of nodes within the network will increase. In that case, it’s quite challenging to upgrade the protocols that align with all parties’ goals in the consortium.
Consortium Blockchain Examples Across Industries
As businesses and companies are catching on to the collaborative potentials of consortium blockchain, it is gradually making its mark in various fields; healthcare, supply chain, logistics, food, finance, energy, etc. to name a few.
Here are some prominent examples of consortium blockchain across diverse industries-
Ripple
Ripple, with its native token named XRP, is an efficient consortium blockchain platform for fast and economic cross-border transactions. It’s also widely used in real-time gross settlement. Due to XRP’s notable dominance in the cryptocurrency market, some major financial institutions use Ripple as their consortium, including American Express, Bank of America, SBI Remit, PNC Bank, etc.
Hyperledger
Another prominent example of a consortium blockchain is Hyperledger, launched by Linux Foundation in 2015. It basically collaborates with companies who develop blockchain tools and networks for industrial usage, supply chain or fintech, for instance. Companies like Cisco, Hitachi, IBM, JP Morgan, Fujitsu, etc. are currently using this platform to electrify their potential.
IBM Food Trust
By bringing numerous participants in the food supply chain together, this platform serves as a major consortium blockchain network in the food industry. The list of members includes growers, processors, distributors, and retailers aiming at transparency and traceability.
R3 Corda
For swift, secure, and confidential financial transactions, institutions are relying on R3 Corda, a dependable consortium blockchain network promoting privacy and security. As well, it offers a variety of advantages to the finance industry by minimizing operational threats, simplifying procedures, and ensuring smooth communications.
Energy Web Foundation
The Energy Web Foundation (EWF) is a non-profit organization, practicing blockchain consortium to cater to the global energy sector by providing blockchain-based solutions. This platform primarily focuses on inter-organizational cooperation, clean energy, stakeholder data security, performance growth, and cost reduction.
Quorum
Quorum is a consortium blockchain framework for enterprises seeking Ethereum-based smart contract solutions. J.P. Morgan designed this open-source platform to facilitate smart contracts and private transactions across industries including healthcare, finance, supply chain, etc.
Final Words
The gist of a consortium blockchain is, however, blending the best features of both private and public blockchains, it offers economic benefits to corporations that collaborate.
Being partially decentralized, it creates a captivating mechanism for businesses comprising both decentralization and control.
In other words, consortium blockchain is all set to revolutionize industrial growth by designing a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for collaborative data management.
Consequently, industries are welcoming its multifaceted applications with open arms, and now, it’s time for you to take advantage of this open-source platform for your organization.




