
Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0 – The Differences and Why Its Important
The internet has come a long way since its inception. From the static web pages of Web 1.0 to the interactive platforms of Web 2.0, the way we access and consume information online has undergone a dramatic transformation.
But what’s next?
Web 3.0 is on the horizon, promising a new era of decentralization, user ownership, and a more democratic web.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, exploring the potential of this emerging paradigm and its impact on the future of the internet.
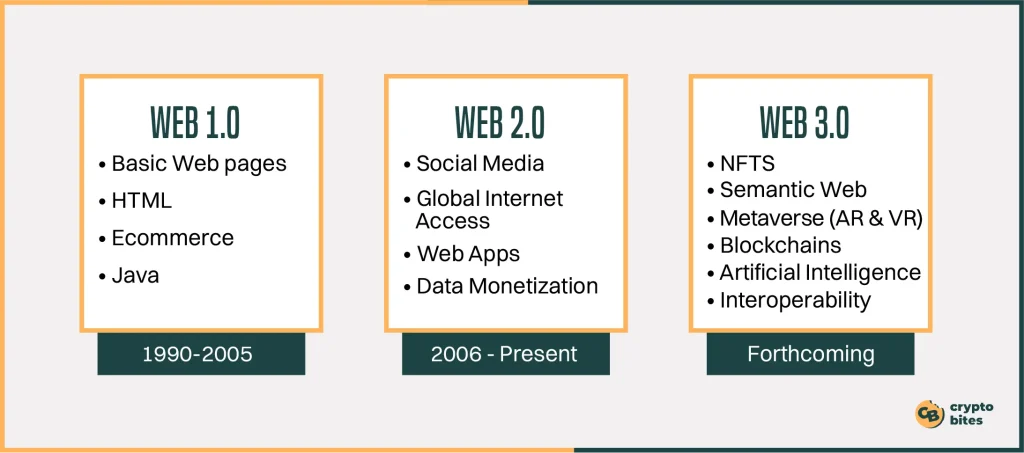
What is Web 1.0?
Web 1.0 refers to the earliest stage of the World Wide Web, often called the “read-only web”. It existed from the mid-1990s to the early 2000s and was characterized by static web pages with limited user interaction.
Here are some of the key features of Web 1.0:
- Static content: Web pages were mostly hand-coded and didn’t change frequently. They were like digital brochures, offering information but not much in the way of engagement.
- Limited user interaction: There were few ways for users to interact with websites. There weren’t any comment sections, social media feeds, or dynamic content like we see today.
- Content creators: Content creation was limited to a select few with the technical knowledge to build websites. The average user could only consume information, not contribute to it.
Think of Web 1.0 as a vast digital library where you could access information, but you couldn’t check out a book, write in the margins, or start your own discussion group.
Web is Web 2.0?
Web 2.0 refers to the current state of the internet, compared to the earlier Web 1.0. It’s characterized by a much more user-centric experience, with features like:
- User-generated content: This is the big difference from Web 1.0. Social media platforms, blogs, wikis, and other sites allow users to create and share their own content. You’re not just reading a digital brochure, you’re part of a conversation.
- Ease of use: Web 2.0 websites are designed to be user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and features that make it easy for anyone to participate.
- Participatory culture: Web 2.0 encourages interaction and collaboration among users. Social media feeds, comments sections, and forums allow users to connect with each other and share ideas.
- Interoperability: Web 2.0 applications and services are designed to work well together. You can share content across different platforms, and data can be easily integrated between different applications.
Think of Web 2.0 as a giant online community center. You can browse information, contribute your own ideas, connect with others who share your interests, and participate in discussions. It’s a much more dynamic and interactive experience than the Web 1.0 days.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0, envisioned as the next generation of the web, focuses on decentralization, where power shifts from big tech companies to users through blockchain technology. This allows users more control over their data and online experiences.
- Decentralization: Unlike Web 2.0, which is dominated by large tech companies, Web3 aims to distribute power among users. Data and applications wouldn’t be controlled by a single entity, but rather spread across a network of computers. This could potentially reduce censorship and increase user privacy.
- Blockchain technology: Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies, is expected to play a central role in Web3. Blockchains are essentially digital ledgers that can securely store and track information. They could be used to manage digital identities, ownership of digital assets, and facilitate secure transactions.
- User control: In Web3, users are supposed to have more control over their data. This means you could decide who has access to your information and how it’s used.
It’s important to note that Web3 is still in its early stages of development, and there’s no guarantee it will take the shape envisioned by its proponents. However, it represents an exciting possibility for a more democratic and user-centric internet.
Comparison Table
Benefits of Web 2.0
Web 2.0, the current state of the internet, offers a vast array of benefits. It focuses on user generated content and has a ton of customizability.
Let’s look at some of them in detail:
1. Increased User Interaction
Remember when the internet was just websites you could read but not really interact with? Web 2.0 changed that. Now you can:
- Become content creators: Blogging platforms like WordPress saw a surge, with over 70 million active websites today (https://wordpress.com/), allowing anyone to share their voice.
- Engage in conversation: Social media comments and forums are the new watercooler chats, letting you discuss everything from cat videos to the latest news. A 2023 Pew Research Center study revealed that 72% of online adults in the US use social media, highlighting its pervasive nature
- Collaborate and share: Wikis like Wikipedia, with over 63 million articles in English alone, demonstrate the power of collective knowledge creation.
2. Rise of Social Networks
Web 2.0 gave birth to social media giants like Facebook (almost 3 billion monthly users!) and Twitter (over 436 million monthly tweets as of last year). These platforms changed how we connect:
- Global connections: Now you can chat with friends and family across the world, making the world feel a lot smaller.
- Career central: LinkedIn (with over 830 million members!) lets you network with people in your field and maybe even land your dream job.
- Find your tribe: Social media groups connect you with people who share your interests, whether it’s dog lovers, gamers, or fans of a specific band.
3. User-Generated Content
Web 2.0 lets anyone be a content creator, not just big companies. Take YouTube, for example, with over 2.5 billion monthly viewers! This has some cool benefits:
- Different voices, different stories: We’re not stuck with information from just a few sources anymore. User-generated content gives us a wider range of perspectives and experiences.
- Anyone can play: If you have an internet connection, you can share your ideas! This leads to a constant flow of fresh content and new formats like vlogs and podcasts.
4. Data-Driven Optimization
The vast amount of user-generated data on Web 2.0 fuels the engine of big data and analytics. Companies leverage this data to:
- Personalized User Experiences: Recommend products tailored to user preferences or curate news feeds that align with their interests.
- Service Improvement: Analyze user behavior to identify areas for improvement and enhance the overall online experience.
- Unveiling Online Trends: Track user engagement and preferences to gain insights into broader societal shifts and consumer
Benefits of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is emerging as a new paradigm for the internet, characterized by a shift towards decentralization and user empowerment. Here’s a deeper dive into its potential benefits, along with some interesting statistics:
1. User Data Ownership and Control (Mastery)
- Current State: In Web 2.0, major tech companies like Facebook and Google control vast amounts of user data, often raising privacy concerns. A 2023 Pew Research Center study found that 81% of Americans believe the benefits of personalized advertising don’t outweigh the privacy risks.
- Web 3.0 Vision: Web 3.0 aims to return ownership and control of data back to users. Imagine storing your data on a secure, decentralized network, accessible only by authorized applications with your permission.
2. Transparency and Openness
- Current State: Many Web 2.0 platforms operate as “black boxes,” making their decision-making processes opaque.
- Web 3.0 Vision: Web 3.0 leverages decentralized networks built on blockchain technology. Blockchain ledgers are public and immutable, potentially fostering greater transparency in how online systems function.
3. Increased Resilience
- Current State: Centralized servers can be vulnerable to outages or attacks, disrupting online services.
- Web 3.0 Vision: Web 3.0’s decentralized nature distributes data and applications across a peer-to-peer network. This redundancy could make online services more resistant to disruptions. A 2022 CloudCamp report estimates that a single hour of downtime for a major cloud service provider costs businesses an average of $100,000.
4. Enhanced Personalization
- Current State: Web 2.0 personalization often feels intrusive, with ads following you across the web.
- Web 3.0 Vision: With user-controlled data, Web 3.0 could enable a new level of personalization. Imagine applications that tailor experiences to your specific needs and preferences, without compromising your privacy.
5. Smarter Web with AI and Machine Learning
- Current State: AI is already present in Web 2.0 applications, but it’s often limited by centralized data silos.
- Web 3.0 Vision: Web 3.0, with its interconnected data structure, could unlock the full potential of AI. Machine learning algorithms could analyze vast datasets across the web, leading to more intelligent and intuitive user experiences.
6. Greater Privacy
- Current State: Web 2.0 platforms are notorious for data collection and targeted advertising.
- Web 3.0 Vision: The decentralized structure of Web 3.0, with user-controlled data, has the potential to offer greater privacy. Users could choose what data to share and with whom, reducing reliance on centralized platforms.
7. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Current State: Traditional finance can be slow, complex, and exclusionary.
- Web 3.0 Vision: Web 3.0 paves the way for DeFi, a new financial system built on blockchain technology. DeFi applications could offer faster, more secure, and accessible financial services for everyone. The global DeFi market reached a value of over $300 billion in December 2023, according to CoinMarketCap.
Web 3.0 is a work in progress, but it holds immense promise for a more democratic, secure, and user-centric future of the internet.
Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0 – Comparison Table
| Feature | Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
| User Interaction | Increased interaction through blogging, social media, and user-generated content. | Potential for even deeper interaction with semantic web technologies and a more immersive user experience. |
| Rise of Social Networks | Pioneered by platforms like Facebook and Twitter, social media connects people globally and fosters communities. | May see decentralized social networks that offer more control over user data and privacy. |
| User-Generated Content | Democratized content creation with platforms like YouTube and Wikipedia. | Empowers users to own and monetize their content directly. |
| Data-Driven Optimization | Uses user data for personalized experiences, service improvement, and trend analysis. | Focuses on user control over data, with potential for privacy-preserving personalization and collaborative data analysis. |
| Data Ownership | Data is controlled by large tech companies, raising privacy concerns. | Aims to give users ownership and control over their data through decentralized storage solutions. |
| Transparency | Decision-making processes of major platforms are often opaque. | Blockchain technology in Web 3.0 can potentially increase transparency through public and immutable ledgers. |
| Resilience | Centralized servers can be vulnerable to outages. | Decentralized nature of Web 3.0 could make online services more resistant to disruptions. |
| Personalization | Personalized experiences can feel intrusive due to data tracking. | Aims for user-centric personalization based on controlled data sharing. |
| AI and Machine Learning | Limited by data silos in centralized systems. | Interconnected data structure could unlock the full potential of AI for more intelligent and intuitive experiences. |
| Privacy | Web 2.0 platforms are known for data collection and targeted advertising. | Decentralized structure with user-controlled data has the potential for greater privacy. |
| Finance | Traditional finance can be slow, complex, and exclusionary. | DeFi (Decentralized Finance) in Web 3.0 offers faster, more secure, and accessible financial services. (Global DeFi market over $300 billion in Dec 2023). |
Bottom Line
The internet we know today is on the cusp of a major transformation. Web 3.0 promises a more democratic, secure, and user-centric online experience. While still in its early stages, Web 3.0 offers exciting possibilities for data ownership, transparency, and innovation.
As we move towards a more decentralized future, it’s important to stay informed about the potential benefits and challenges that lie ahead.
Web 3.0 has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with the internet, but its success will depend on collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to user empowerment. Are you ready for the next phase of the web?
However, alongside the potential benefits, Web 3.0 also comes with its own set of threats.
Security breaches, manipulation of data, and the lack of established regulations are just some of the concerns that need to be addressed. Just as users take more control of their data, they will also need to take on more responsibility for its security.




