What Is A Key Characteristic Of The Peer-To-Peer Networking Model?
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
Decentralization, it is! Instead of relying on a central server, this decentralized architecture runs through direct data sharing and communication within the nodes, providing each of them equal control.
More than being yet another term, peer-to-peer networking has become a revolutionary concept in recent years, reshaping digital collaboration in a new light.
Nowadays, it’s more mainstream than you can even imagine, and you have most likely participated in one too (maybe without realizing it).
Think of downloading files, sharing music with friends, or contributing to a virtual group project. A P2P technology might be the driving force behind all of these digital collaborations.
That being said, the global P2P marketplace is projected to hit $8474.8 million by 2034.
Intrigued? Let’s explore the essence of peer-to-peer networking including its key features, advantages, disadvantages, and more.
What Is a Peer-to-Peer Network? How Does It Work?
A peer-to-peer network is defined as a decentralized communication model without a dedicated central authority.
The devices within the network, addressed as peers/nodes, are directly interconnected to share resources, not relying on any intermediary intervention.
Unlike a traditional client-server model, where there’s a dedicated server to house data and resources, all nodes across the network get equal privileges here.
That means each device in a P2P ecosystem can work both as a client and a server, while processing requests from others and issuing requests to other peers, respectively.
Imagine five friends working on a group project as a real-world peer-to-peer network example.
Here, all the group members are equally responsible for finishing the task.
They don’t rely on a trainer/instructor to lead the way.
Rather, all five friends directly share relevant data and information with each other to contribute to the project.
Most importantly, the absence of one friend doesn’t affect the project, as other members actively participate in the task.
Group discussion, sharing relevant materials, asking questions to clarify doubts- all these happen without any third-party involvement.
This is how peer-to-peer networks run between peers, sharing data, files, or services directly without storing them centrally.
Even if a peer fails to communicate, others can still collaborate to keep the system functioning, making the network more resilient.
What Are the Key Characteristics of a P2P Networking Model?
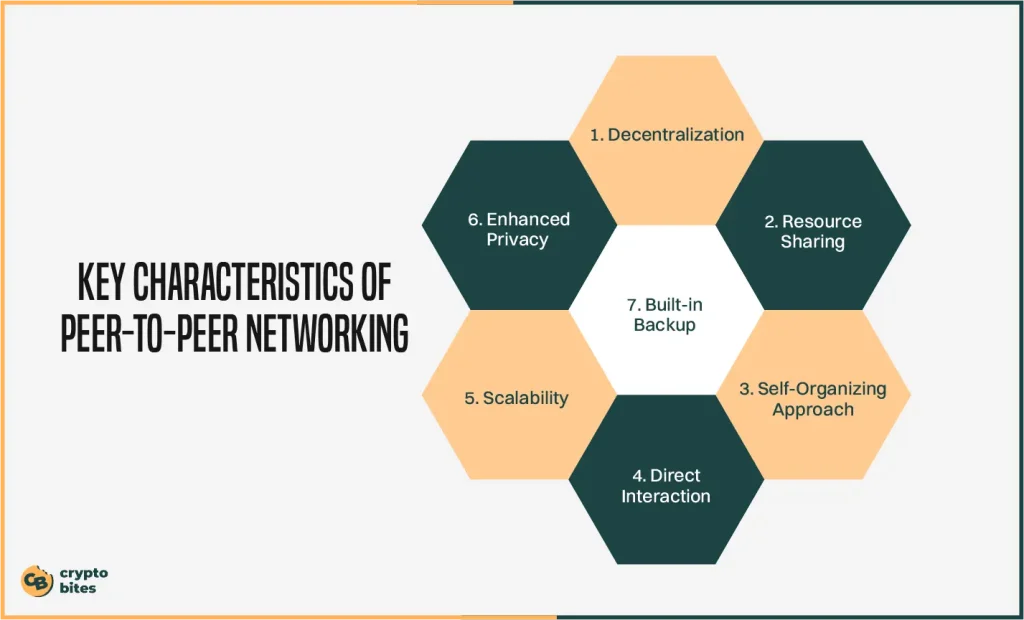
Alongside decentralization, the key characteristic of peer-to-peer networking, some other fundamental features also contribute to its success, making P2P the core of the modern networking landscape.
Here, I will break down its key traits to show you a clearer view:
1. Decentralization
In a modern P2P landscape, the decentralized approach makes the entire system failure-proof.
Imagine having a central hub where all files and resources are stored. (Yes, I am talking about the traditional approach of data sharing)
Now, if the hub catches fire, is there a way to save those resources?
That’s where decentralization stands out without a single point of failure, as no central authority controls the network here.
Instead, all participants equally own the system, sharing both its capabilities and responsibilities.
2. Resource Sharing
Resource sharing is yet another key feature of a P2P ecosystem.
Here, nodes/peers share their personal resources within the network- bandwidth, data storage, and processing power, to name a few.
This mutual contribution allows efficient use of resources, making the network reach its full potential.
On one hand, it lessens the burden on an individual member or any central server.
On the other hand, it fosters trust and community bonding within the nodes, leading to better cooperation in the future.
3. Self-Organizing Approach
Remember the first boy band you formed at school? And then the lead guitarist suddenly gets transferred to another school, making the entire band fall apart?
You can forget the fear now! The self-organizing peer-to-peer network doesn’t work that way.
It has a self-driven, adaptable approach that doesn’t get affected by leaving members.
Instead, peers can join/leave at will, and the system will automatically reorganize its protocol.
If one peer fails to communicate or leaves the network, others can still run the show, as all have equal dominance and functionality over the system.
4. Direct Interaction
The best examples of direct P2P interaction are instant messaging, voice calling, video calling, etc.
This eliminates the need to rely on a middleman, alongside facilitating faster, real-time communication.
Unlike a traditional approach (with intermediaries), the modern peer-to-peer model offers easier and more effective interaction these days.
Imagine buying a book from an online marketplace vs buying it directly from the seller.
Certainly, the second option offers a more personalized experience while allowing direct contact (and contract) with the seller.
5. Scalability
As opposed to the regular client-server model, P2P networks are inherently scalable, and here are the reasons:
- With more peers added to the network, it organically becomes more scalable with more capacity
- Every peer comes with new resources instead of depending on a central server
- The absence of dedicated infrastructure with a fixed capacity lets the network handle higher loads
- P2P models follow a distributed approach in data management, resulting in no overloading issues
No wonder BitTorrent relies on the P2P protocol for file sharing, as it handles larger amounts of traffic at a time.
6. Enhanced Privacy
When you directly interact with a peer, there’s no central authority to monitor the contact.
Given that, the information exchanged in a peer-to-peer communication is more confidential.
Even the shared resources within the network are only accessible by authorized peers.
So, it’s undoubtedly a great way of encrypted data exchange, enhancing privacy and security.
7. Built-in Backup
With no central point of control, the P2P ecosystem is free of a single point of failure.
Thus, it’s inherently robust and resilient, not taking down the entire system because of the failure of one peer.
Take a library for example, where it works as the central server to issue books to readers (clients).
Now, what if the library burns down? All the books will be gone, right?
In contrast, in peer-to-peer networking, each member within the community shares their individual book collections, resulting in a distributed approach to avoid such mishaps.
Even if a single member is unavailable, others can still share their books within the network to continue the operation.
Advantages of a Peer-to-Peer Network
Here are the core advantages of decentralized P2P networking:
- P2P network operates directly among peers, eliminating the need for an expensive server
- No network manager required to monitor its workflow
- Each node, with personal computers, reduces operation costs by resource-sharing
- You can easily set this model at homes or in small businesses
- Decentralized infrastructure allows faster download and upload from multiple peers at a time
Peer-to-Peer Communication: The Challenges
With a plethora of benefits, the modern P2P architecture also comes with some challenges as follows:
- Peers can’t centrally backup shared data and resources, they are only available within the network
- With no central authority, it requires more involvement from the nodes to maintain network security, integrity, and performance
- A large number of nodes leaving the network at once will result in limited resources, thereby putting a strain on the network’s overall functionality
- Illegal sharing of copyrighted content within a P2P network can raise serious legal and ethical concerns
Major Applications of P2P Architecture
Now, let’s explore the pivotal role of P2P architecture in some relevant areas-
1. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Two of the most widespread applications of P2P networking are blockchain and cryptocurrency.
The fun fact is, these are closely interrelated.
Cryptocurrency uses a peer-to-peer network for transferring digital currencies, like bitcoin, and blockchain records that transaction through a decentralized and distributed ledger.
Following the core mechanism of a P2P system, cryptocurrency facilitates direct fund transfer between users without any middleman’s intervention.
2. File Sharing
As I discussed above, BitTorrent is a famous file-sharing platform that relies on P2P architecture.
Here, users can download and upload files simultaneously, without depending on a central server.
If you are a BitTorrent user, you can either directly download files from others, or upload your existing file for other users to download it.
3. Instant Messaging
If we talk about the most popular instant messaging apps of recent times, Messenger, Skype, and WhatsApp would certainly make it to the top of the list.
In fact, WhatsApp claims the crown with 2 billion monthly active users.
However, these applications are based on peer-to-peer communication, enabling users to communicate with each other without any centralized dominance directly.
4. Collaborative Computing
P2P networks also introduced collaborative computing, where multiple peers work together to solve complex problems.
Thus all nodes across the network collectively contribute to the overall analysis of the task.
5. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Another example of a P2P application is Content Delivery Networks, which follow P2P protocol to share content more effectively.
In these networks, you can share content with others that you have already access to, resulting in minimum server load and faster delivery.
6. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Unlike the regular financial ecosystem, Decentralized Finance promotes independence in financial operations for more transparency.
But how? By leveraging the basic P2P principle which allows for decentralized decision-making, without any financial institutions (like banks) being involved.
The Future of P2P: Does a Decentralized Tomorrow Await?
Since its emergence in the 1990s, P2P networking has undergone a lot of changes.
However, with the growing technological landscape, it will face more challenges for unfailing data management.
Naturally, we need a more secure data-sharing approach that demonstrates scalability, resilience, and redundancy.
And decentralization, the key characteristic of a peer-to-peer networking model, is the future of a data-driven tomorrow, ensuring security and user empowerment instead of centralized control.
So, be a part of this brighter tomorrow by embracing the P2P potential today!




